Alumina/Resin-Rubber Bonded Abrasive Blade
Alumina/Resin-Rubber Bonded Abrasive Blade
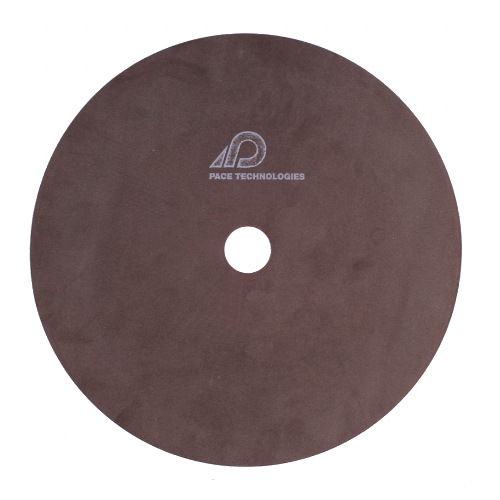
Pace Technologies, MAX-A250, 10" x 0.039" x 32 mm Alumina/Resin-Rubber Bonded Abrasive Blade (MOS 4580 rpm) (Universal Thin Blade)Abrasive Blade Selection Guidelines Selecting the correct abrasive blade is dependent upon the design of the cut-off machine and, to a large extent, the operator preference. Abrasive blades are generally characterized by their abrasive type, bond type and hardness. Determining the correct blade is dependent upon the material or metal hardness and whether it is a ferrous or a nonferrous metal.Abrasive sectioning has primarily been used for sectioning ductile materials. Examples include metals, plastics, polymer matrix composites, metal matrix composites, plastics and rubbers. The proper selection of an abrasive blade requires an understanding of the relationship between the abrasive particle, abrasive bonding and the specimen properties.Recommended Abrasive Cutting ProceduresSelect the appropriate abrasive blade.Secure specimen. Improper clamping may result in blade and/or specimen damage.Check coolant level and replace when low or excessively dirty. Note abrasive blades break down during cutting and thus produce a significant amount of debris.Allow the abrasive blade to reach its operating speed before beginning the cut.A steady force or light pulsing action will produce the best cuts and minimize blade wear characteristics, as well as maintain sample integrity (no burning).When sectioning materials with coatings, orient the specimen so that the blade is cutting into the coating and exiting out of the base material, thereby keeping the coating in compression. Unit of MeasurePack of 10 pcs. ... Show More Show Less

 Copied
Copied